Optimizing Filtration: Understanding How Liquid Viscosity Affects Filter Bag and Cartridge Applications
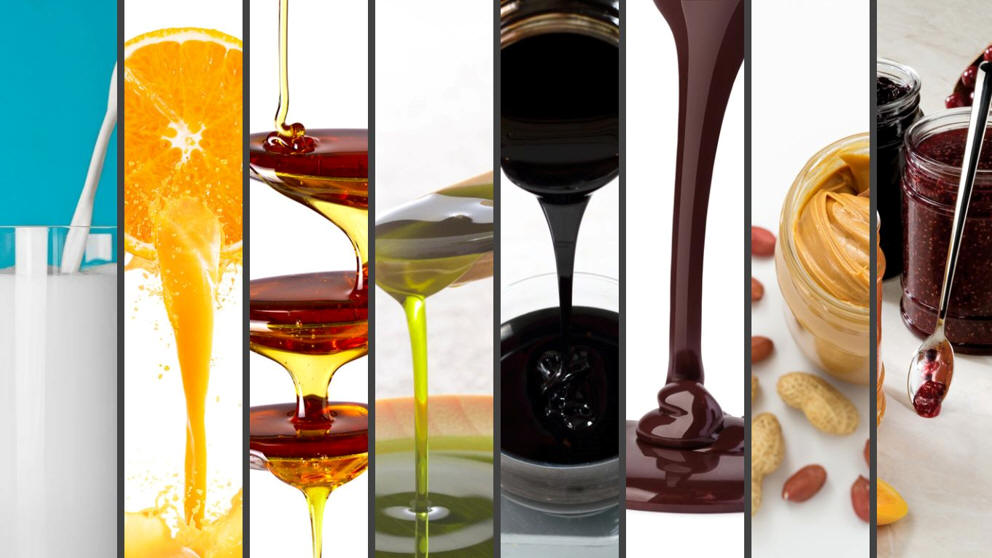

Filtration is an essential process across various
industries, serving to purify liquids and remove contaminants for downstream
applications. Choosing the right filtration method, whether using filter
bags or filter cartridges, is critical to achieving optimal performance. One
of the key factors influencing this decision is the viscosity of the liquid
being filtered, especially if it differs significantly from water. Viscosity
is a measure of a liquid's resistance to flow and thus impacts the
filtration process, including liquid velocity and differential pressure.
This article explains the relationship between liquid viscosity and
filtration, the advantages of filter bags or filter cartridges in different
scenarios, and some examples of common high and low viscosity liquids
filtered with filter bags and filter cartridges.
Understanding the
Impact of Liquid Viscosity on Filtration
Viscosity plays a fundamental
role in liquid filtration as it affects how the liquid flows through the
filter media. Liquids with higher viscosity have thicker and slower flows at
a given pressure, while low-viscosity liquids exhibit thinner and faster
flows at that same pressure. This difference in viscosity significantly
influences liquid velocity and differential pressure across the filter
media.

Liquid Velocity
In the context of liquid
filtration, liquid velocity refers to the speed at which the liquid flows
through the filter media. High-viscosity liquids experience reduced flow
velocities due to their inherent resistance. As these liquids traverse the
filter media, they must overcome the small pores and interstitial spaces,
resulting in slower movement and lower liquid velocities.
This is
problematic for both filter bag and filter cartridge filtration because it
can contribute to uneven flow distribution across the media. It can be
off-set somewhat by operating at a higher pressure and thus filter
cartridges might be a better choice due to their inherent ability to handle
higher differential pressures.
There are filter bag designs, such as
Eaton’s MAX-LOAD, which have comparable differential pressure ratings but
also offer the advantage of higher flow rate capacities and increased
surface area in support of less frequent media replacement and an overall
simpler housing design.
Bag filter housings are designed to
accommodate accessories which filter cartridge housings are not, namely
liquid displacement balloons and magnetic inserts. The displacement balloons
would help even-out the liquid distribution and for applications where
magnetic inserts are desired, the increased residence time amplifies their
effectiveness.
Differential Pressure
Differential pressure is the
pressure difference between the inlet and outlet sides of the filter.
High-viscosity liquids tend to generate higher differential pressures for a
given flow rate due to their increased resistance while passing through the
filter media. If the liquid is conveyed with a positive displacement pump
system, the flow rate will remain constant as the differential pressure
increases and the velocity through the filter media will increase as the
open area is reduced. Centrifugal pump and other fluid delivery systems may
deliver less flow with an increase in differential pressure, reducing the
liquid velocity and perhaps effecting the downstream process with the
reduced flow rate.
Filter Cartridges: Ideal for High Viscosity
Liquids
The high viscosity applications in which filter cartridges are
commonly used have a couple of characteristics besides higher differential
pressure tolerance that favor filter cartridge designs: lower flow rates and
necessity to retain finer solids.

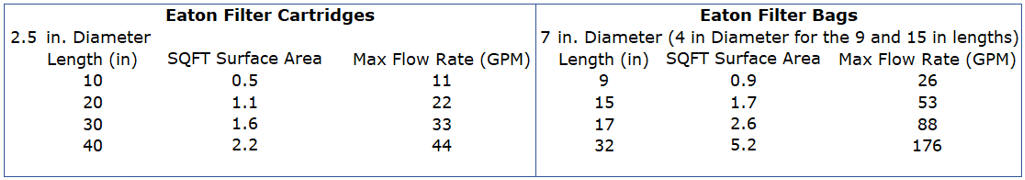
Single filter cartridge systems are limited in flow
rate to approximately 1 GPM per inch of length and the longest filter
cartridges offered through Eaton are 40” long. If the flow rate is
significantly higher than 40 GPM, it might be more cost effective to use a
single filter bag housing design compared to a multiple filter cartridge
design in terms of initial cost and ongoing cost related to media
replacement.
Filter bag designs that have similar maximum
differential pressure capabilities as filter cartridges are limited in their
filtration efficiency and size of particles which can be retained. Filter
cartridges tend to be more efficient and there are many designs for
submicron levels of filtration.
Therefore, if the flow rates are on
the higher end and a nominal >1 micron particle retention is required,
filter bags might be the most cost-effective solution whereas filter
cartridges provide more options for higher efficiency retention of finer
particle sizes and are especially cost effective for <40 GPM flow rate
applications.
Advantages of Filter Bags in Versatile Applications
While filter cartridges are advantageous in specific scenarios, filter bags
have advantages as well.
Larger Surface Area
Filter bags generally
have a larger surface area compared to individual filter cartridges. This
attribute makes them highly effective for filtering low to moderate
viscosity liquids. Thus, for the higher flow rate applications where
sufficient liquid velocity is available, the increased surface area
increases the duration between media replacement. This also contributes to
maintaining a lower differential pressure and perhaps a more consistent flow
rate.
Cost-Effectiveness
Filter bags are
typically less costly for high flow rate applications because filter
cartridge systems often require multiple cartridges to handle higher flow
rates which can be accommodated by a single filter bag. This is especially
true for applications which require nominal filtration efficiency of
particles >1 micron as the cost for complex filter bags with absolute rated
efficiency are quite expensive and more susceptible to damage via higher
differential pressures.
Specialized Accessories
Filter bag systems
offer various accessories, such as displacement balloons and magnetic
inserts, which can enhance filtration performance in specific applications.
Displacement balloons reduce the liquid retained within the filter bag and
inadvertently help maintain a higher velocity across the filter bag surface;
they reduce loss of process liquid due to media change-outs. Filter
cartridge systems generally retain less unfiltered liquid, so the addition
of displacement balloons to bag filter systems enable you to benefit from
the other aspects of filter bags while reducing loss of process liquid.
Magnetic separators are very powerful magnetic assemblies that reside
within the center of filter bags and they significantly increase the
retention efficiency of ferrous particles. Magnetic separators will extend
the duration between media changes for any liquids that contain high levels
of ferrous particles and benefit any application for which such metal fines
are problematic. There is no equivalent magnetic separation for industrial
filter cartridges.
Complexity and Cost Considerations
Higher flow
rate applications can be accommodated with a smaller filter vessel size and
use fewer filter units when using a filter bag housing. The inherent higher
capacity of filter bags (up to 4x the flow rate of the largest filter
cartridge offered by Eaton) results in less sealing points within the
vessel; the simplification of design lowers the cost of the vessel, and
contributes to less downtime for replacing clogged media.
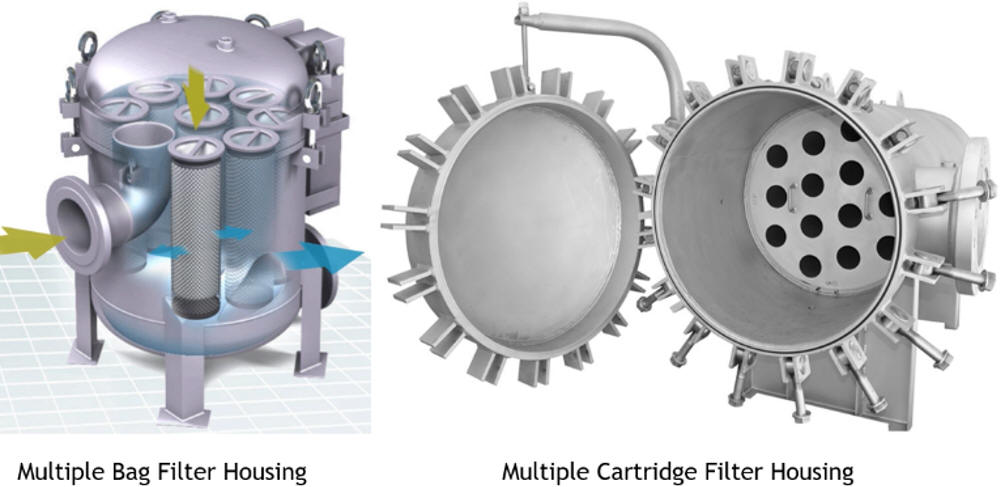
Filter bags are often more cost effective than
filter cartridges, although there are less options for applications having
higher differential pressures or applications which require high efficiency
submicron particle retention.
Conclusion
Selecting the right
filter bag or filter cartridge style depends on the viscosity of the liquid
and the specific requirements of the filtration process. Filter cartridges
excel in handling higher viscosity liquids with elevated differential
pressures and finer solids, making them suitable for specific applications.
Certain models are designed to withstand higher liquid temperatures and
others are designed to mitigate fiber migration of the filter media itself.
On the other hand, filter bags offer larger surface areas and
cost-effectiveness, making them a versatile choice for most applications
involving low to moderate viscosity liquids. Understanding the impact of
liquid viscosity on filtration helps make informed decisions, ensuring
optimal filtration performance in diverse industrial settings. Whether it's
filter bags or filter cartridges, choosing the right filtration method is
crucial to achieving efficient and effective liquid purification.




